SpringCloud_Gateway系列(二)-源码分析
初始化流程
初始化类
SpringCloud_Gateway的配置类主要有三个:
- GatewayAutoConfiguration:(单独介绍)
- GatewayClassPathWarningAutoConfiguration:这个配置类主要是校验作用。当我们的项目中是使用的SpringMvc时会触发警告。或者当项目没有包含Spring Webflux也会触发warn
- GatewayLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration:主要是配置负载均衡
GatewayAutoConfiguration
初始化Netty相关配置,这里不深入看了。这玩意我目前还看不懂以后再来看
初始化各种GatewayFilterFactory
就是这一堆
初始化各种RoutePredicateFactory
初始化各种GlobalFilter
初始化RouteDefinitionLocator和RouteLocator
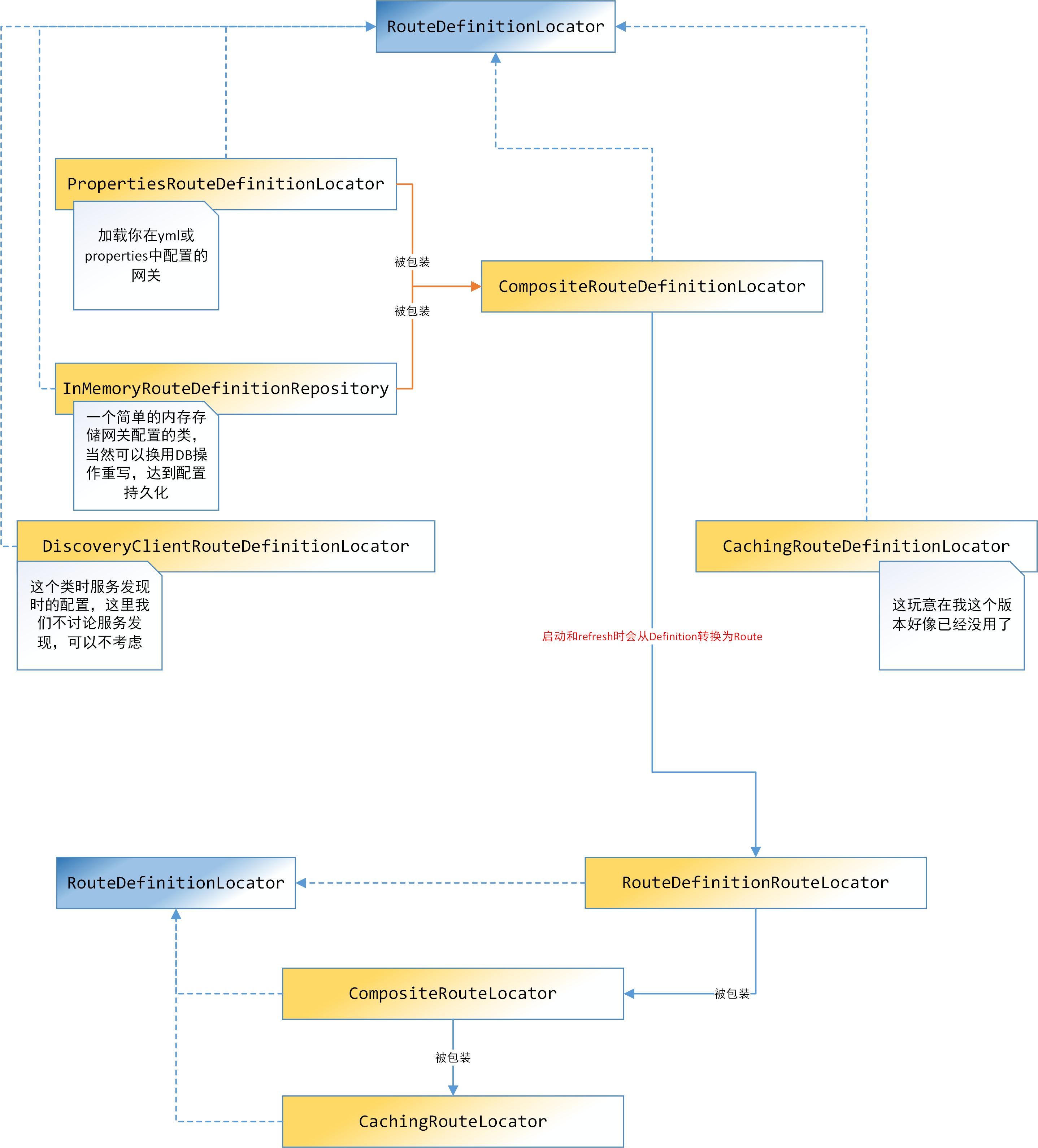
RouteDefinitionLocator主要有3个:- PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator是负责加载yml或者properties中配置的路由信息
- InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository是一个口子,实现了RouteDefinitionRepository这个接口,我们可以自己实现RouteDefinitionRepository接口,达到从内存,Redis,各种DB,或者云化Config(比如YY的cnt)拉取配置的目的
- DiscoveryClientRouteDefinitionLocator 这个类是用来从DiscoverClient整合路由信息的。DiscoveryClient目前spring支持Eureka,Zookeeper,Consul.可以自己选用。我们这里不想带入服务发现,暂时不分析。
当3个RouteDefinitionLocator加载完成后,会被包装为一个CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator。这个组合Locator是route和routeDefinition转换的中间站。
RouteDefinitionLocator实现也有3个:
- RouteDefinitionRouteLocator:核心类之一,RouteDefinition转换为Route
- CompositeRouteLocator:包装RouteDefinitionRouteLocator
- CachingRouteLocator:包装CompositeRouteLocator,会在第一次运行后,cache转换后的route
初始化FilteringWebHandler
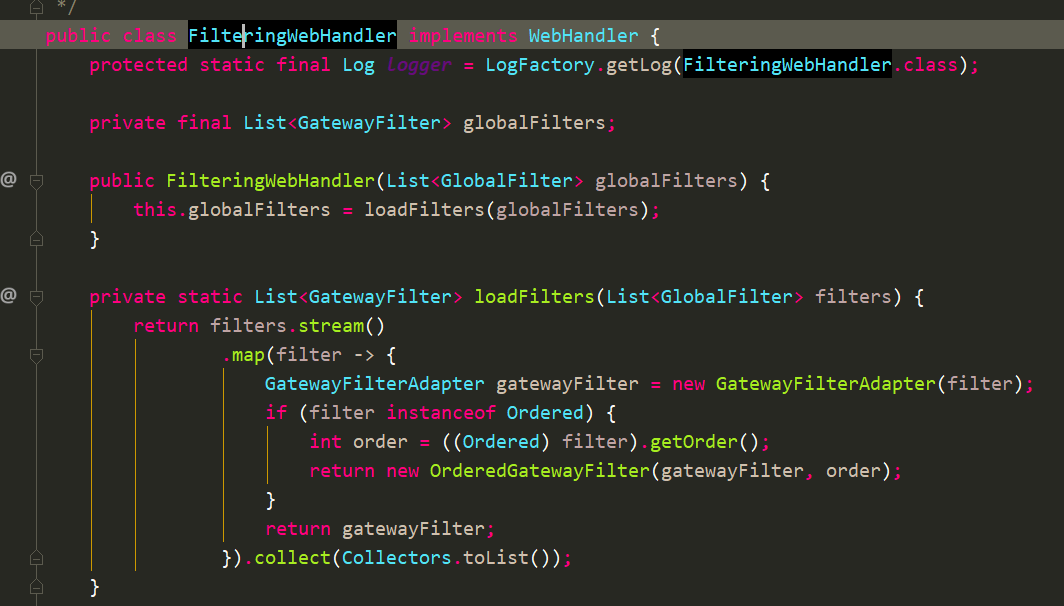
实现WebHandler,是filter chain的入口。会把GlobalFilter转换为GatewayFilter。运行时会combine初始化RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping的类继承关系图
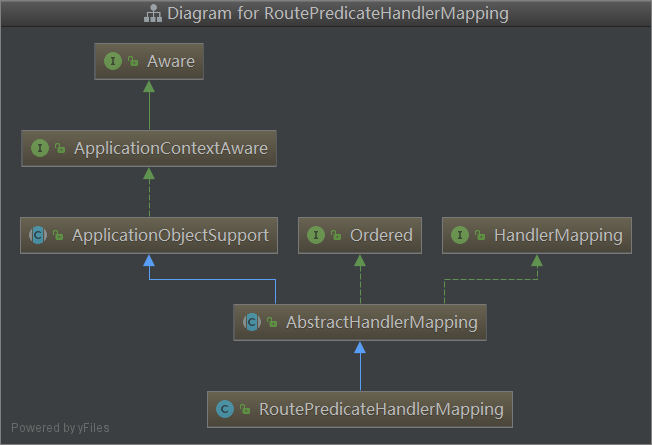
可以看到RoutePredicateHandlerMapping实现了HandlerMapping接口。在DispatcherHandler中,会对HandlerMapping进行操作。这里是整个spring webflux和spring cloud gateway整合的入口。
看过springMvc的朋友可能对DispatcherHandler这个类很熟悉,对的,你没有猜错。spring webflux中也是叫这个名字。Spring Cloud Gateway 入口就在concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange))这里。
@Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest(); logger.debug("Processing " + request.getMethodValue() + " request for [" + request.getURI() + "]"); } if (this.handlerMappings == null) { return Mono.error(HANDLER_NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION); } return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings) .concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange)) .next() .switchIfEmpty(Mono.error(HANDLER_NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION)) .flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler)) .flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result)); }初始化RouteRefreshListener
RouteRefreshListener主要是用来动态更新Route信息类。是我们动态更新route的核心。在我们这个系列(三)中我们会详细介绍。
运行时流程
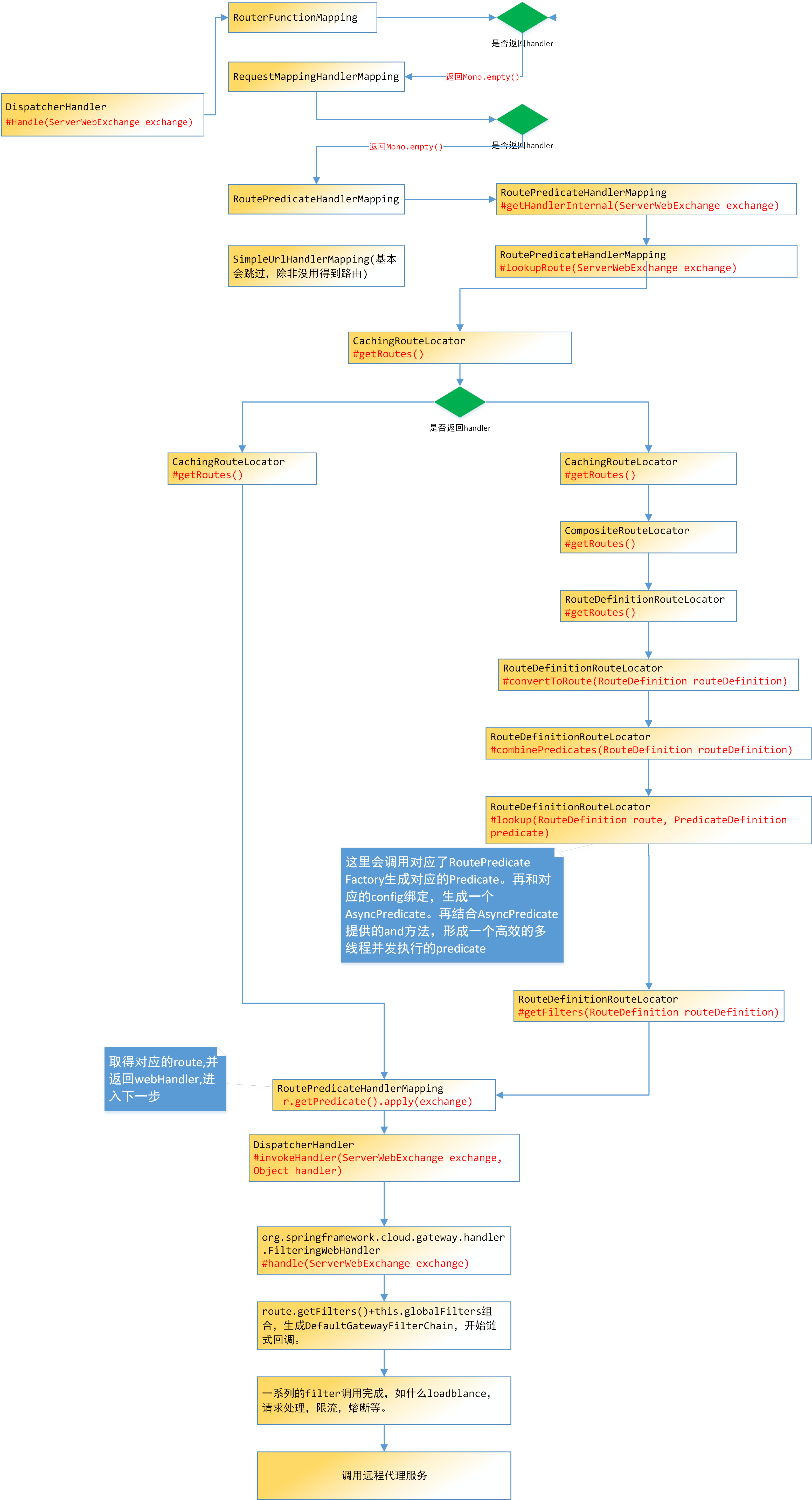
在DispatcherHandler handle请求
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest(); logger.debug("Processing " + request.getMethodValue() + " request for [" + request.getURI() + "]"); } if (this.handlerMappings == null) { return Mono.error(HANDLER_NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION); } return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings) .concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange)) .next() .switchIfEmpty(Mono.error(HANDLER_NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION)) .flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler)) .flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result)); }这里是spring webflux和spring cloud gateway交互入口。this.handlerMappings一般一共有4个,当我们匹配到RoutePredicateHandlerMapping时,返回FilteringWebHandler,触发next().不再调用其他的mapping,然后就会invokeHandler,handleResult等。
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping

mapping.getHandler(exchange))会调用到AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler方法@Override public Mono<Object> getHandler(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return getHandlerInternal(exchange).map(handler -> { if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(exchange.getRequest())) { CorsConfiguration configA = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(exchange); CorsConfiguration configB = getCorsConfiguration(handler, exchange); CorsConfiguration config = (configA != null ? configA.combine(configB) : configB); if (!getCorsProcessor().process(config, exchange) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(exchange.getRequest())) { return REQUEST_HANDLED_HANDLER; } } return handler; }); }由此进入到RoutePredicateHandlerMapping的getHandlerInternal(ServerWebExchange exchange)中。
@Override protected Mono<?> getHandlerInternal(ServerWebExchange exchange) { exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_HANDLER_MAPPER_ATTR, getClass().getSimpleName()); return lookupRoute(exchange) // .log("route-predicate-handler-mapping", Level.FINER) //name this .flatMap((Function<Route, Mono<?>>) r -> { exchange.getAttributes().remove(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Mapping [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "] to " + r); } exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR, r); return Mono.just(webHandler); }).switchIfEmpty(Mono.empty().then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> { exchange.getAttributes().remove(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No RouteDefinition found for [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "]"); } }))); }核心是lookupRoute(exchange)
protected Mono<Route> lookupRoute(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return this.routeLocator .getRoutes() //individually filter routes so that filterWhen error delaying is not a problem .concatMap(route -> Mono .just(route) .filterWhen(r -> { // add the current route we are testing exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR, r.getId()); return r.getPredicate().apply(exchange); }) //instead of immediately stopping main flux due to error, log and swallow it .doOnError(e -> logger.error("Error applying predicate for route: "+route.getId(), e)) .onErrorResume(e -> Mono.empty()) ) // .defaultIfEmpty() put a static Route not found // or .switchIfEmpty() // .switchIfEmpty(Mono.<Route>empty().log("noroute")) .next() //TODO: error handling .map(route -> { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Route matched: " + route.getId()); } validateRoute(route, exchange); return route; }); }这里this.routeLocator..getRoutes()会调用CachingRouteLocator拿到缓存下来的route。然后执行过滤r.getPredicate().apply(exchange)。lambda表达式的r就是route。
这里的r.getPredicate()得到的AsyncPredicate方法很有艺术性。可以深入学习一下(见第4小节:AsyncPredicate生成)第一次路由初始化cache流程
我们看一下CachingRouteLocator实现,有个很好用的代码部分
public class CachingRouteLocator implements RouteLocator { private final RouteLocator delegate; private final Flux<Route> routes; private final Map<String, List> cache = new HashMap<>(); public CachingRouteLocator(RouteLocator delegate) { this.delegate = delegate; routes = CacheFlux.lookup(cache, "routes", Route.class) .onCacheMissResume(() -> this.delegate.getRoutes().sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE)); } @Override public Flux<Route> getRoutes() { return this.routes; } /** * Clears the routes cache * @return routes flux */ public Flux<Route> refresh() { this.cache.clear(); return this.routes; } @EventListener(RefreshRoutesEvent.class) /* for testing */ void handleRefresh() { refresh(); }这里构造函数中的这段代码很有意思
routes = CacheFlux.lookup(cache, "routes", Route.class) .onCacheMissResume(() -> this.delegate.getRoutes().sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE));这里提供一种Flux流缓存构造方式,他的意思是,当cache没有的时候,我们执行this.delegate.getRoutes().sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE)获得Flux流,并把这个结果写入cache这个Map。这不会马上执行,当有subscribe才会执行。是懒加载方式。
当我们缺少缓存时,this.delegate.getRoutes()将会调用CompositeRouteLocator的getRoutes()方法
@Override public Flux<Route> getRoutes() { return this.delegates.flatMap(RouteLocator::getRoutes); }然后就会进入RouteDefinitionRouteLocator的getRoutes()方法。这个方法是一个核心的方法。负责把所有routeDefinition转换为route。是连接RouteDefinitionLocator和RouteLocator的通道。
@Override public Flux<Route> getRoutes() { return this.routeDefinitionLocator.getRouteDefinitions() .map(this::convertToRoute) //TODO: error handling .map(route -> { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("RouteDefinition matched: " + route.getId()); } return route; }); }直接进入核心方法convertToRoute
private Route convertToRoute(RouteDefinition routeDefinition) { AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate = combinePredicates(routeDefinition); List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters = getFilters(routeDefinition); return Route.async(routeDefinition) .asyncPredicate(predicate) .replaceFilters(gatewayFilters) .build(); }这个方法有两个子方法,第一个是combinePredicates会把routeDefinition带有的predicate组合成为一个AsyncPredicate。(见4.AsyncPredicate生成)还有得到gatewayFilters(见5.gatewayFilters生成)。然后调用Route的build接口生成Route。最后存入cache。
AsyncPredicate生成
当我们调用combinePredicates方法时,会得到AsyncPredicate。
private AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> combinePredicates(RouteDefinition routeDefinition) { List<PredicateDefinition> predicates = routeDefinition.getPredicates(); AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate = lookup(routeDefinition, predicates.get(0)); for (PredicateDefinition andPredicate : predicates.subList(1, predicates.size())) { AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> found = lookup(routeDefinition, andPredicate); predicate = predicate.and(found); } return predicate; }这里循环调用lookup方法,再用and连接起来。
private AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> lookup(RouteDefinition route, PredicateDefinition predicate) { RoutePredicateFactory<Object> factory = this.predicates.get(predicate.getName()); if (factory == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to find RoutePredicateFactory with name " + predicate.getName()); } Map<String, String> args = predicate.getArgs(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("RouteDefinition " + route.getId() + " applying " + args + " to " + predicate.getName()); } Map<String, Object> properties = factory.shortcutType().normalize(args, factory, this.parser, this.beanFactory); Object config = factory.newConfig(); ConfigurationUtils.bind(config, properties, factory.shortcutFieldPrefix(), predicate.getName(), validator); if (this.publisher != null) { this.publisher.publishEvent(new PredicateArgsEvent(this, route.getId(), properties)); } return factory.applyAsync(config); }这里会根据predicate的name,得到对应的RoutePredicateFactory,比如name=StripPrefix就会得到StripPrefixGatewayFilterFactory。在调用ConfigurationUtils.bind方法,把predicate的配置与工厂绑定,调用factory.applyAsync(config)生成AsyncPredicate。
default AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> applyAsync(C config) { return toAsyncPredicate(apply(config)); }关键方法toAsyncPredicate
public static AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> toAsyncPredicate(Predicate<? super ServerWebExchange> predicate) { Objects.requireNonNull(predicate, "predicate must not be null"); return t -> Mono.just(predicate.test(t)); }至此,predicate变成了AsyncPredicate。但是一个route配置了多个不同的predicate怎么组合的。
我们看看AsyncPredicate源码public interface AsyncPredicate<T> extends Function<T, Publisher<Boolean>> { default AsyncPredicate<T> and(AsyncPredicate<? super T> other) { Objects.requireNonNull(other, "other must not be null"); return t -> Flux.zip(apply(t), other.apply(t)) .map(tuple -> tuple.getT1() && tuple.getT2()); } default AsyncPredicate<T> negate() { return t -> Mono.from(apply(t)).map(b -> !b); } default AsyncPredicate<T> or(AsyncPredicate<? super T> other) { Objects.requireNonNull(other, "other must not be null"); return t -> Flux.zip(apply(t), other.apply(t)) .map(tuple -> tuple.getT1() || tuple.getT2()); } }看看and方法
return t -> Flux.zip(apply(t), other.apply(t)) .map(tuple -> tuple.getT1() && tuple.getT2());短短的一句话,包括了多线程执行,再把所有执行结果 “&&”操作。zip这个方法很精辟。这就是rx架构的精髓。
gatewayFilters生成
调用getFilters(routeDefinition),也会由名字找到对应factory生成gatewayFilter,再触发bind绑定。但是不同的是,这里会给没有order的filter加上order
ArrayList<GatewayFilter> ordered = new ArrayList<>(filters.size()); for (int i = 0; i < filters.size(); i++) { GatewayFilter gatewayFilter = filters.get(i); if (gatewayFilter instanceof Ordered) { ordered.add(gatewayFilter); } else { ordered.add(new OrderedGatewayFilter(gatewayFilter, i + 1)); } }invokeHandler流程
直接看代码吧
private Mono<HandlerResult> invokeHandler(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) { if (this.handlerAdapters != null) { for (HandlerAdapter handlerAdapter : this.handlerAdapters) { if (handlerAdapter.supports(handler)) { return handlerAdapter.handle(exchange, handler); } } } return Mono.error(new IllegalStateException("No HandlerAdapter: " + handler)); }这里会调用到SimpleHandlerAdapter的handle方法。
@Override public Mono<HandlerResult> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Object handler) { WebHandler webHandler = (WebHandler) handler; Mono<Void> mono = webHandler.handle(exchange); return mono.then(Mono.empty()); }传入的handler就是org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.FilteringWebHandler。
@Override public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) { Route route = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR); List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters = route.getFilters(); List<GatewayFilter> combined = new ArrayList<>(this.globalFilters); combined.addAll(gatewayFilters); //TODO: needed or cached? AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(combined); logger.debug("Sorted gatewayFilterFactories: "+ combined); return new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(combined).filter(exchange); }组合全局filter加上route域的filter。生成DefaultGatewayFilterChain。开始回调所有的filter。
走完filter就是调用目标服务,返回代理信息。源码分析结束。老哥们,是不是看的很累。